Choosing between Intel’s Core i5 and Core i7 processors can be a daunting task, especially with the rapid evolution of CPU technology. Both offer distinct advantages depending on your needs, budget, and workload. To help you decide, let’s break down their differences across key factors like performance, efficiency, and value.
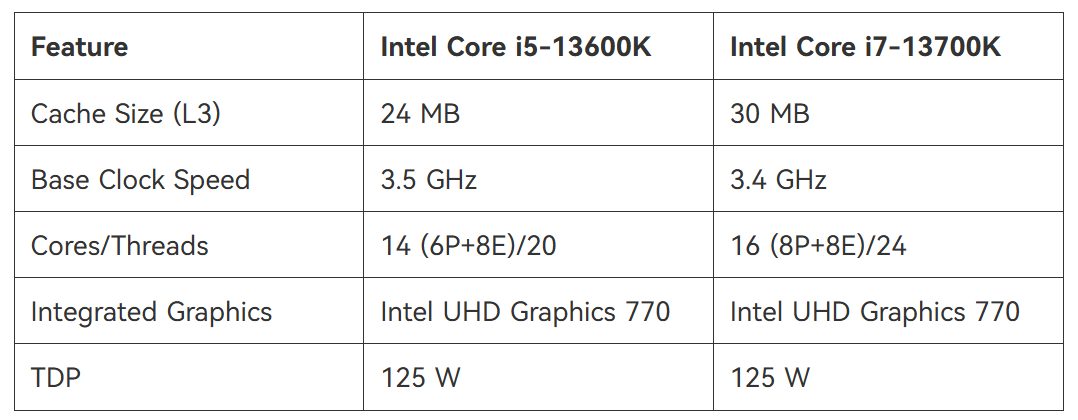
The most significant difference lies in core and thread configurations. Core i7 processors typically feature more physical cores and support Hyper-Threading, a technology that allows each core to handle two threads simultaneously. For example, an i7-13600K boasts 16 cores and 24 threads, while a comparable i5-13600K offers 14 cores and 20 threads. This makes the i7 superior for multithreaded workloads like video rendering, 3D modeling, or running virtual machines.
Hyper-Threading, however, has limited impact on everyday tasks like web browsing or office work. If your workflow relies on single-threaded applications, even an i5 with a slightly higher base clock (e.g., 3.9 GHz vs. 3.6 GHz) might perform similarly.
Cache memory plays a critical role in reducing data latency. Core i7 processors generally have larger L3 caches—16 MB vs. 12 MB in the 11th-gen i5—which accelerates repetitive tasks like code compilation or large dataset processing. For instance, in benchmarks like Cinebench R20, the i7’s cache advantage translates to 15–20% faster multi-core performance.
For gamers, the choice depends on resolution and GPU pairing. At 1440p or 4K, where the GPU handles most work, even a mid-tier i5 (e.g., 12th-gen i5-12600K) delivers nearly identical frame rates to an i7-12700K in AAA titles like Cyberpunk 2077 or Horizon . However, competitive esports titles like CS:GO or Rainbow Six Siege may see a 5–7% boost with an i7 due to higher clock speeds and thread optimization.
If you’re building a budget-friendly rig, an i5 paired with a powerful GPU often provides better value. Save the extra cost for a higher-tier graphics card.
Core i7’s performance comes at a cost: higher power consumption. For laptops, this impacts battery life and thermal management. Thin-and-light laptops with i7 processors may throttle under sustained loads due to limited cooling, negating their performance edge. In contrast, i5-based systems are more energy-efficient and better suited for ultrabooks or portable workstations.
Desktop users should also consider cooling solutions. High-end i7 CPUs often require robust air or liquid cooling to maintain stability during intensive tasks.
The i5 shines in cost-effectiveness. A 12th-gen i5-12600K costs 40–50% less than an i7-12700K but delivers 90% of its gaming performance. For productivity, the i7’s premium is justified only if you regularly use software like Adobe Premiere Pro or Blender that leverages extra cores.
Budget-conscious users can allocate savings toward faster RAM, an SSD, or a better GPU—upgrades that often yield more noticeable improvements.
If longevity is a priority, the i7’s additional cores and threads offer better future-proofing. As software increasingly optimizes for multicore performance (e.g., AI tools, 8K video editing), an i7 will stay relevant longer. For example, Intel’s 12th-gen hybrid architecture (P-cores and E-cores) in i7 CPUs ensures compatibility with next-gen applications.
Choose Core i5 if:
Your tasks include gaming, office work, or light content creation.
You prioritize budget efficiency and lower power consumption.
You’re building a compact system with limited cooling.
Choose Core i7 if:
You work with professional-grade software (e.g., CAD, 4K video editing).
You multitask heavily or run virtual machines.
You want a system that remains performant for 5+ years.
The Intel Ultra 7 is also a great choice if you want to further improve your PC’s performance, read further if interested: Intel Core Ultra 7 vs i7: Which One Is Best For You
Intel’s Core i5 and i7 cater to different audiences, and the “better” CPU depends on your specific use case. While the i7 dominates in raw power, the i5 remains a smart choice for most users. Always consider generational improvements—newer i5 models often outperform older i7s, so “buying new” can sometimes trump tier differences.
We also have other series of mini computers, such as the C0B series of N100, for more information click the picture below
More Useful Resources
1.How Much RAM Do You Need for a Mini PC?
2.How Important is Energy Efficiency When Choosing a Mini PC?
3.Building a Quiet and Efficient Workstation with a Mini PC

Click to confirm
Cancel